
Pi Pico C/C++ SDK 환경에서 GPIO토글 속도 측정 결과와 비교해서 Arduino 환경보다 빠른것 같은데 SPI 속도도 측정해서 비교해 보자
W6100과 같은 SPI의 전송 속도가 이더넷 전송률에 영향을 미치는 어플리케이션을 위해 SDK환경에서 SPI 테스트를 해 둘 필요가 있을것 같다.
SDK 환경에서 SPI 전송 테스트를 해보면 SPI Bye 전송 지연은 680ns로 Arduino 환경과 비슷하게 측정이 된다.

#include <stdio.h>
#include "pico/binary_info.h"
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#include "hardware/spi.h"
#include "hardware/uart.h"
// SPI Defines
// We are going to use SPI 0, and allocate it to the following GPIO pins
// Pins can be changed, see the GPIO function select table in the datasheet for information on GPIO assignments
#define SPI_PORT spi0
#define PIN_MISO 16
#define PIN_CS 17
#define PIN_SCK 18
#define PIN_MOSI 19
void spi_initialize(void)
{
spi_init(SPI_PORT, 37.5 * 1000 * 1000);
gpio_set_function(PIN_SCK, GPIO_FUNC_SPI);
gpio_set_function(PIN_MOSI, GPIO_FUNC_SPI);
gpio_set_function(PIN_MISO, GPIO_FUNC_SPI);
// make the SPI pins available to picotool
bi_decl(bi_3pins_with_func(PIN_MISO, PIN_MOSI, PIN_SCK, GPIO_FUNC_SPI));
}
int main()
{
unsigned char buffer[10];
stdio_init_all();
// SPI initialisation.
spi_initialize();
// Chip select is active-low, so we'll initialise it to a driven-high state
gpio_init(PIN_CS);
gpio_set_dir(PIN_CS, GPIO_OUT);
gpio_put(PIN_CS, 1);
gpio_init(25);
gpio_set_dir(25, GPIO_OUT);
gpio_put(25, 0);
while (true) {
spi_write_blocking(SPI_PORT, buffer, 2);
spi_write_blocking(SPI_PORT, buffer, 2);
}
}
옵티마이즈 옵션을 최대로 해서 측정해 보자
# Add executable. Default name is the project name, version 0.1
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} -O3")
컴파일 옵티마이즈후 SPI Byte전송 지연이 48ns로 빨라 졌다. Arduino 환경에서 DMA를 사용한것과 거의 동일하게 빨라 졌다.
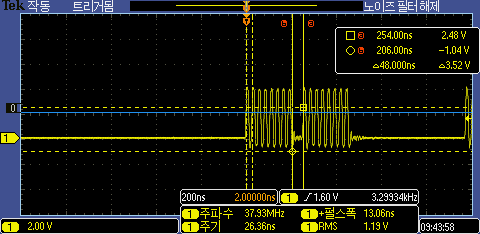
그렇다면 DMA를 사용한다면 더 빨라 지려나?
RP2350에서 SPI DMA를 이용한 전송 테스트를 해 보자
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pico/binary_info.h"
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#include "hardware/spi.h"
#include "hardware/uart.h"
// SPI Defines
// We are going to use SPI 0, and allocate it to the following GPIO pins
// Pins can be changed, see the GPIO function select table in the datasheet for information on GPIO assignments
#define SPI_PORT spi0
#define PIN_MISO 16
#define PIN_CS 17
#define PIN_SCK 18
#define PIN_MOSI 19
#define USE_SPI_DMA
#ifdef USE_SPI_DMA
#include "hardware/dma.h"
static uint dma_tx;
static uint dma_rx;
static dma_channel_config dma_channel_config_tx;
static dma_channel_config dma_channel_config_rx;
void spi_write_dma(uint8_t *pBuf, uint16_t len)
{
uint8_t dummy_data;
channel_config_set_read_increment(&dma_channel_config_tx, true);
channel_config_set_write_increment(&dma_channel_config_tx, false);
dma_channel_configure(dma_tx, &dma_channel_config_tx,
&spi_get_hw(SPI_PORT)->dr, // write address
pBuf, // read address
len, // element count (each element is of size transfer_data_size)
false); // don't start yet
channel_config_set_read_increment(&dma_channel_config_rx, false);
channel_config_set_write_increment(&dma_channel_config_rx, false);
dma_channel_configure(dma_rx, &dma_channel_config_rx,
&dummy_data, // write address
&spi_get_hw(SPI_PORT)->dr, // read address
len, // element count (each element is of size transfer_data_size)
false); // don't start yet
dma_start_channel_mask((1u << dma_tx) | (1u << dma_rx));
dma_channel_wait_for_finish_blocking(dma_rx);
}
#endif
void spi_initialize(void)
{
spi_init(SPI_PORT, 37.5 * 1000 * 1000);
gpio_set_function(PIN_SCK, GPIO_FUNC_SPI);
gpio_set_function(PIN_MOSI, GPIO_FUNC_SPI);
gpio_set_function(PIN_MISO, GPIO_FUNC_SPI);
// make the SPI pins available to picotool
bi_decl(bi_3pins_with_func(PIN_MISO, PIN_MOSI, PIN_SCK, GPIO_FUNC_SPI));
#ifdef USE_SPI_DMA
dma_tx = dma_claim_unused_channel(true);
dma_rx = dma_claim_unused_channel(true);
dma_channel_config_tx = dma_channel_get_default_config(dma_tx);
channel_config_set_transfer_data_size(&dma_channel_config_tx, DMA_SIZE_8);
channel_config_set_dreq(&dma_channel_config_tx, DREQ_SPI0_TX);
// We set the inbound DMA to transfer from the SPI receive FIFO to a memory buffer paced by the SPI RX FIFO DREQ
// We coinfigure the read address to remain unchanged for each element, but the write
// address to increment (so data is written throughout the buffer)
dma_channel_config_rx = dma_channel_get_default_config(dma_rx);
channel_config_set_transfer_data_size(&dma_channel_config_rx, DMA_SIZE_8);
channel_config_set_dreq(&dma_channel_config_rx, DREQ_SPI0_RX);
channel_config_set_read_increment(&dma_channel_config_rx, false);
channel_config_set_write_increment(&dma_channel_config_rx, true);
#endif
}
int main()
{
unsigned char buffer[10];
stdio_init_all();
// SPI initialisation.
spi_initialize();
// Chip select is active-low, so we'll initialise it to a driven-high state
gpio_init(PIN_CS);
gpio_set_dir(PIN_CS, GPIO_OUT);
gpio_put(PIN_CS, 1);
gpio_init(25);
gpio_set_dir(25, GPIO_OUT);
gpio_put(25, 0);
while (true) {
#ifdef USE_SPI_DMA
spi_write_dma(buffer, 2);
spi_write_dma(buffer, 2);
#else
spi_write_blocking(SPI_PORT, buffer, 2);
spi_write_blocking(SPI_PORT, buffer, 2);
#endif
sleep_ms(10);
}
}
DMA 사용시 48ns로 10배이상 빨라진다.

옵티마이즈 했을 경우 DMA 블럭 전송 지연은 440ns로 측정이 된다.

옵티마이즈 옵션을 사용하지 않으면 6200ns로 느려진다.

반응형



